TIG or Laser Welding Machine – Which One Should You Choose?
Hello everyone, I hope through this article you can understand the differences between TIG welding and laser welding, so that you can choose the most suitable welding machine for your workshop or company.This is the video of TIG VS Laser welding ,if you want to see , can click here .
Index.
1、What is a TIG welding machine?
2、What is a laser welding machine?
3、Comparison between the two machines
4、Who are these two machines suitable for?
5、Frequently asked questions
1、What is a TIG welding machine?

TIG = Tungsten Inert Gas Welding.Also known as argon arc welding (GTAW).
It uses a tungsten electrode and argon gas. It is suitable for stainless steel and aluminum.
Advantages of TIG Welding
A:High weld quality
Fine and delicate weld seam
Attractive weld appearance
B:Precise welding control
Current can be adjusted accurately
Penetration depth can be controlled
C:Wide range of applicable materials
Stainless steel
Aluminum alloy
Copper
Nickel alloy
Titanium
D:High welding strength
With skilled operation, the weld quality is very stable.
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
A:Slow welding speed
Low production efficiency, especially for batch processing.
B:High skill requirement for operators
Requires coordination of both hands
Requires long-term training
Highly dependent on skilled welders
C:Large heat-affected zone
Prone to deformation
Thin sheets are easy to burn through
D:High post-processing cost
Weld seam turns black
Stainless steel requires grinding and polishing
E:High fatigue during long working hours
High labor intensity for welders
Not suitable for high-intensity continuous production
Applications of TIG Welding
A:Small processing workshops
Door and window fabrication
Railings and handrails
Stainless steel decorative parts
B:Automotive repair industry
Exhaust pipes
Modification welding
C:Kitchen equipment manufacturing
Stainless steel sinks
Commercial kitchen equipment
D:Precision industries
Aerospace
Medical devices
Pipeline welding
E:Aluminum product processing
Aluminum frames
Aluminum housings
2、What Is a Laser Welding Machine?

A laser welding machine is a high-precision welding system that uses a concentrated laser beam as a heat source to join metal materials together.
Unlike traditional welding methods such as TIG or MIG, laser welding uses a focused light beam to create deep and narrow weld seams with minimal heat distortion.
The core principle of laser welding:
A:The laser source generates a high-energy laser beam
B:The laser is transmitted to the welding head through an optical fiber
C:The beam is focused on the metal surface
D:The metal melts instantly to form a molten pool
E:After cooling, a weld seam is formed
Because the laser energy is highly concentrated:
Deeper penetration
Narrower weld seam
Less deformation
Main components of a laser welding machine.
Laser source
Welding head
Control system
Cooling system
Main advantages of laser welding machines:
A:Fast welding speed
Usually 3–5 times faster than TIG
B:Small heat-affected zone
Reduces deformation
C:Attractive weld seam
No extensive grinding required
D:Easy to operate
Lower skill requirement for welders
E:Suitable for automated production
Materials suitable for laser welding:
Stainless steel
Carbon steel
Aluminum
Galvanized sheet
Brass
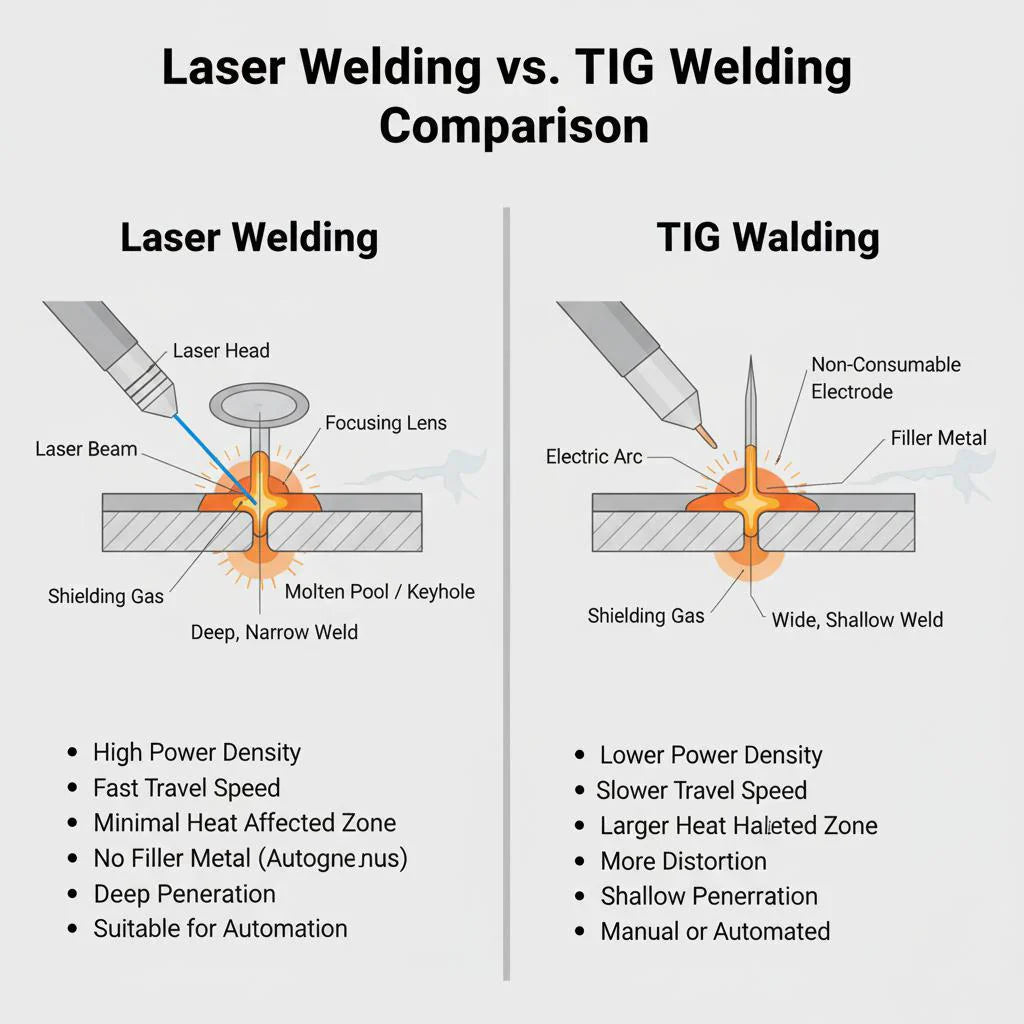
3、Comparison between the two machines
| Comparison Item | TIG Welding | Laser welding |
| Welding Speed | Slower | 3-5 times faster |
| Weld Quality | Possible discoloration (oxidation), widerweld bead | Smooth, narrow and clean weld seam |
| Heat Affected Zone | Larger heat input, more distortion | Minimal heat input, less deformation |
| Operator Skill Requirement | Requires skilled and experienced welder | Easier to learn and operate |
| Production Efficiency | Suitable for small batches | Ideal for mass production |
| Machine Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
| Labor Cost | Higher long-term labor cost | Lower labor dependency |
| Post-Processing | Often requires grinding and polishing | Minimal or no post-processing |
Speed comparison data.
| Material | Thickness | TIG Speed | Laser Speed |
| Stainless steel | 1mm | 0.5-0.8 m/min | 2-4 m/min |
| Stainelss steel | 2mm | 0.3-0.5 m/min | 1.5-3 m/min |
| Carbon steel | 3mm | 0.2-0.4 m/min | 1-2 m/min |
4、Who are these two machines suitable for?
Who is TIG suitable for?
Small batch production
Limited budget
Repair work
Who is laser welding suitable for?
Mass production
High efficiency requirements
Businesses that do not want to rely heavily on skilled welders
5、Frequently asked questions
A:Can laser welding replace TIG welding?
In many industrial applications, yes.
Laser welding is faster and produces cleaner welds, especially for stainless steel and thin sheet metal.
B:Is laser welding stronger than TIG?
Both processes can produce strong welds.
Laser welding provides deeper penetration and smaller heat affected zones, which can improve structural performance in certain applications.
C:Does laser welding require shielding gas?
Yes.
Just like TIG welding, laser welding requires shielding gas (usually argon or nitrogen) to protect the molten metal from oxidation.
D:Is laser welding difficult to operate?
Compared to TIG welding, laser welding is easier to learn and requires less operator skill.
E:Is laser welding more expensive?
The machine cost is higher, but labor cost and production time are significantly reduced.




